Africa: the Potential Arms-sell Competition among the EU, Russia and China?
In
Log in if you are already registered
Russia, China, the five members of European Union (France, Germany, the UK, Spain, and Italy) take the 66 percent of international arms transfer in the period of 2009~2013 (Siemon T. Wezeman, 2014). Compared with the 2004~2008, the percentage of arms importers of major weapon regional, Africa increase from 7% to 9% in the same period (see the below). As recipient, the poorly limited defense budget in African continent, will acting as the main obstacle against arms import to the predictable. For the reason of energy supply, geostrategic considerations, the main suppliers have not exclude the bartering oil and mina for weapons, even generous present. For example, Sudan’s purchase capabilities of modern weapons, as such 96-type main-battle tanks, F-7 combat aircrafts are on the basis of its profits of oil export to China.
According to Stockholm data, 1996~2010, Russia and China respectively held the position of No.1 and 2 largest exporter to Africa (Pieter D. Wezeman, 2011). Usually, the arms transfer to Africa has been connected with illicit trade in small arms and light weapons (SALW). However, we should not the fact that the export of major weapon to the reviving continent. “Between 2004~2008 and 2009~13 imports by states in Africa increased by 53 percent” (Siemon T. Wezeman, 2014). For the purpose of maritime security, the acquisition of maritime assets will be taken priority by the most sub-Saharan African states. The sophisticated weapon systems made by Russia and China have been exported to African states, especial Sub-Saharan states. In December, 2013, it is reported that Russia’s state arms export monopoly said that it would deliver 12 Su-30K fighter jets to a nation in southern Africa. Contrary to the past, Chinese defense groups show its ambitions to develop African market with their high-technology weapons. From 2009 t0 present, besides SALW, China-Pakistan joint-manufactured JF-17 represents a potential inroad into this market with the reliability problems can be solved.
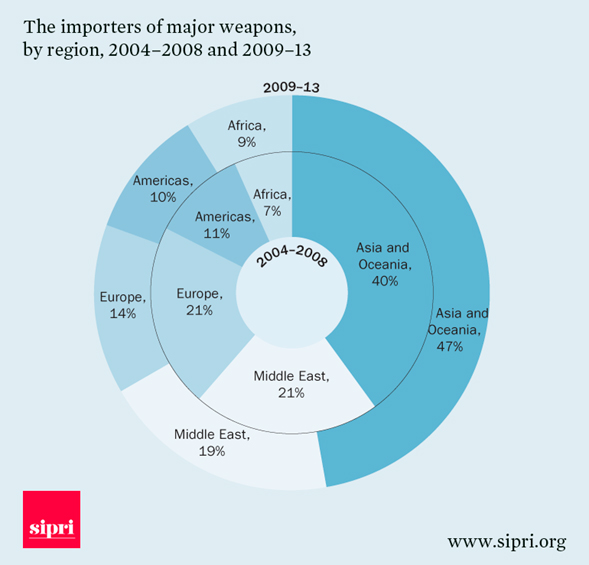
Compared with Russia and China, the European states also have been as a significant player of arms trade with African. “15 EU members exported major arms to sub-Saharan Africa, 7 more exported or licensed the export of the broader category of arms and military equipment, including major arms and SALW” (Pieter D. Wezeman, 2011). Even under the international embargo, some African states accessed the weapons for European countries knowingly exported, transferred, or brokered arms deals for countries that have been under an international arms embargo for all or part of the period between 2005 and 2009, which include the Democratic Republic of Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Eritrea, Liberia, Libya, Sierra Leone, the Darfur region of Sudan, and Somalia. (AEFJN Report, 2010).
African defense market has different meanings for Russian, European and Chinese. For Russia, the incentives seemly major from economic and the symbol as its global player; for European, improve the African state’s defense capabilities can be regarded as the measure to prevent the regional stability and anti-terrorism. For Chinese, the arms export to African means to the diversified energy resources, the leading profile in the developing world, and the geostrategic outflank to India.
Reference:
1. Siemon T. Wezeman and Pieter D. Wezeman, “Trends in International Arms Transfers, 2013”, SIPRI Fact Sheet, March 2014, http://books.sipri.org/files/FS/SIPRIFS1403.pdf.
2. Pieter D. Wezeman, Siemon T. Wezeman and Lucie Béraud-Sudreau, “Arms Flows to Sub-Saharan Africa”, SIPRI Policy Paper No. 30, Dec. 2011, http://books.sipri.org/files/PP/SIPRIPP30.pdf.
3. Africa Europe Faith and Justice Network (AEFJN): “Arms Exports and Transfers: Europe to Africa, by Country”, Dec. 2010, http://www.aefjn.org/index.php/364.html?file=tl_files/aefjnfiles/arms/arms_material%20eng/1101%20AEFJN%20Report%20export%20arms%20Europe%20to%20Africa%20eng.pdf.




